Understanding and Meeting Learners Where They Are using the UDL Lens
CompetencyWorks Blog
 This is the third in a three part series by Kathleen McClaskey, co-author of Make Learning Personal and How to Personalize Learning. Read the first and second posts.
This is the third in a three part series by Kathleen McClaskey, co-author of Make Learning Personal and How to Personalize Learning. Read the first and second posts.
In the CompetencyWorks paper based on the 2017 National Summit on K-12 Competency-Based Education, Designing for Equity, one of the four key issues in advancing competency-based education is “meeting students where they are.” It describes that a high quality competency-based system connects learning in relationships and requires educators to understand their learners as individuals and then select strategies based upon that knowledge. Before we look at how to meet learners where they are, let’s review what has presented in Part 1 and Part 2 of this series.
In Part 1, Universal Design for Learning (UDL) was introduced as the pedagogical approach based on the learning sciences to create an inclusive learning culture with educational equity at the center. In Part 2, we described how using the UDL Lens of Access, Engage and Expresstm can help build the skills of agency and self-advocacy for every learner in addition to creating partnerships in learning, an essential element for a high quality competency-based system. In the this last part of this series, the focus is how do we know where learners are, what do we do once we know where learners are, and how do we move them forward?
In order to meet learner where they are, districts and schools need to create a learning culture that is built from a shared pedagogical philosophy based on the learning sciences that will enable strong partnerships in learning. This learning culture must recognize that every individual is a learner and is valued in the community, and that each learner will have a voice to share ideas and opinions and will be supported to take risks. The next question is…
How do we know where learners are?
In Part 2 of this series, the Learner Profile based on the UDL Lens of Access, Engage and Expresstm was introduced where the learner shares their story of who they are, what they aspire to be, what they care about, and how they learn. Next, teachers have conversations with the learner about strengths, challenges, preferences, and needs and begin to build a better understanding of the learner. Most important in this process is that the learner is sharing what he or she understands about their own learning, for the first time often revealing the social and emotional side of their learning. This new insight of the learner alongside the numerical data that is collected from testing and the data on the competencies they have mastered offers a fuller picture of where the learner is, what skills they need to develop to support their challenges and enhance their strengths that will lead to agency, and what hopes and dreams they may have.
What do we do, once we know?
Once we know who our learners are, we need to consider how we design our lessons and projects, and how we design flexible learning spaces to support the learners and activities in our classrooms each day. Consider…
“Lesson design with all learners in mind!”
Now that we know who our learners and how they learn, the question is how do we take this information about our learners and develop instructional methods, materials, and assessments each day in our lessons and projects so that we are responsive to the way they learn? In an elementary classroom, understanding each learner using the UDL Lens of Access, Engage and Expresstm is an important tool in deciding on the instructional methods, the materials that you will use in a lesson, and the assessments that would be most effective. In a middle school and high school, a Class Learning Snapshot can be applied by taking the Learner Profiles of four learners from both ends of the learning spectrum in your classroom. The learning spectrum in a classroom may span from learners who have cognitive or learning challenges on one end to self-directed learners on the other end. Keeping these four learners in mind will help you better design instruction for the entire class. Todd Rose, author of The End of Average, notes in his 2013 TEDx, The Myth of Average, “Design to the edges and we will reach them.”
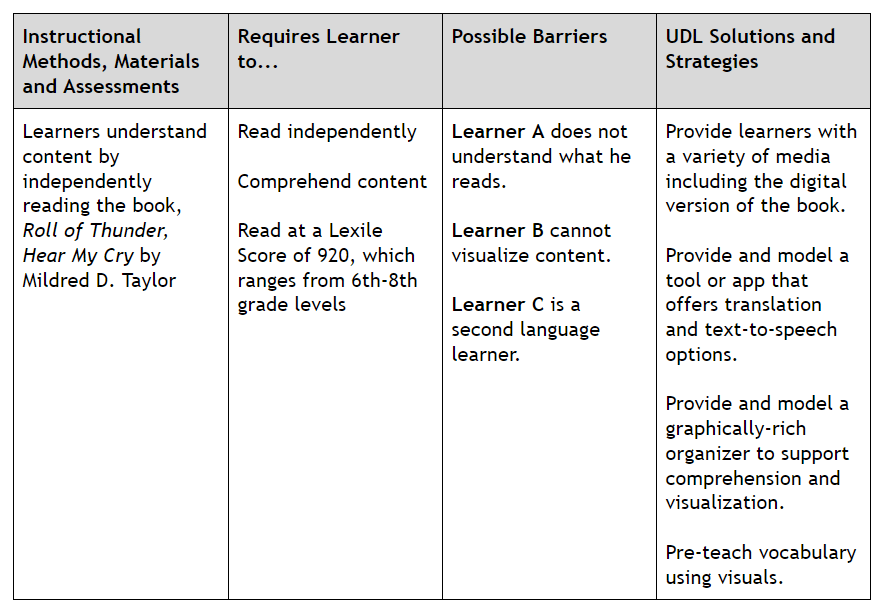
Next, take any lesson and use the Four-Step UDL Lesson Review Process to decide and intentionally design the instructional methods, materials and assessments you will use.
Here is one example of what this four-step process may look like in a sixth grade literature lesson on Roll of Thunder, Hear My Cry by Mildred D. Taylor.
This four-step process, when applied in daily practice, will meet learners where they are by providing every learner access to the curriculum, by including different opportunities to engage with the content, and by offering ways for each learner to express what they know and understand. Above all, by using this four-step process, you are designing your lessons and projects to reduce barriers to learning as well as to optimize the levels of challenge and support to meet the needs of all learners from the start.
If we are to meet learners where they are, then we need to co-design flexible learning environments with our learners to support the variability in their learning and the pace they need to learn. This is where learning spaces are designed for learners to have autonomy in where they need to learn alongside areas for collaboration, creativity, and individual and large group instruction. Having flexible learning spaces consistently offers each learner the opportunity to have the choices in daily activities with the options to work collaboratively, communicate with peers, and engage in critical thinking.
What do we do to move every learner forward?
Once we know where learners are, then next we need to help each of them to develop the knowledge, skills, and dispositions so they can progress in the way they learn and offer ways and opportunities for them to connect with their passions, interests, and aspirations. Using the Learner Profile is the starting point where learners share what their interests are or have been, what they aspire to be, how they want to contribute to make it a better world, or maybe what issues they are passionate about with beliefs that can change the status quo. We need to seek opportunities for each learner to follow their passions, interests, and aspirations so they can find their purpose. For the first time, we have the ability to meet learners where they are, to design and engage learners in the ways that they learn, to design learning spaces that support the learner, and to respond to learners as they learn.
So let’s turn to the essential question in this series: “How can we create an inclusive learning culture with equity at the center?”
Several of the quality design principles highlighted in Designing for Equity are instrumental in creating the environment to meet every learner where they are, move them forward, and create an inclusive learning culture with equity at the center:
- Recognize and nurture every child and adult as a “learner” to create an inclusive learning culture. Culture Design Principle – Equity, Learning and Inclusivity; Structure Design Principle – Educators as Learners.
- Focus on having each learner develop agency and to take ownership of learning so that they can self-advocate, self-regulate, and ultimately self-direct their learning. Keep in mind that in order for ownership of learning to occur, it is required that each learner needs to understand how they learn using the UDL Lens. Teaching and Learning Design Principles – Based on Learning Sciences and Student Agency and Ownership.
- Create a learning orientation classroom where meta-learning is practiced. Meta-learning means “learning about learning” that promotes the ability of a learner to plan, monitor, reflect, and think deeper in one’s learning. (Watkins, 2010). Teaching and Learning Design Principle – Rigorous High Level Skills
- Develop daily practice to help learners make sense of their learning:
- notice learning,
- have conversations about learning,
- reflect on learning, and
- make learning an object of learning. (Watkins, 2011)
- Culture Design Principle – Growth Mindset
- Intentionally design instructional methods, materials and assessments using the UDL Lesson Review Process by understanding the strengths, challenges, preferences, and needs of your learners. Teaching and Learning Design Principle – Responsive; Structure Design Principle – Flexibility
- Establish a system to provide learning opportunities for learners to have experiences inside and outside the classroom that is responsive to their interests, passions, and/or aspirations. Culture Design Principle – Relevance
- Set a goal along with a set of actionable steps in your school or school district this coming year, in collaboration with all stakeholders, to commit in creating an inclusive learning culture with equity at the center. Structure Design Principle – Continuous Improvement and Organizational Learning
The work of educators at the district, school, and classroom level is to keep equity in the center of decision-making. When the UDL Lens is used in daily practice by teachers, learners, and the learning community, equity and inclusivity becomes the learning culture.
*The UDL Lens of Access, Engage and Express is a trademark of Kathleen McClaskey.
References
Bray, B., & McClaskey, K. (2017). How to Personalize Learning: A Practical Guide for Getting Started and Going Deeper. Thousand Oaks: Corwin.
Lopez, N., Patrick, S. and Sturgis, C., Designing for Equity: Leveraging Competency-Based Education to Ensure All Students Succeed, 2018.
Rose, T. (2013, June 19). The Myth of Average: Todd Rose at TEDxSonomaCounty. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4eBmyttcfU4
Watkins, C. (2010). Learning, Performance and Improvement. INSI Research Matters, 34, International Network for School Improvement Web site: http://www.ioe.ac.uk/about/documents/Watkins_10_Lng_Perf_Imp_ev.pdf
Watkins, C. (2011). Learning: a sense-maker’s guide. Professional Development Series, https://www.atl.org.uk/publications-and-resources/classroom-practice-publications/learning-sense-makers-guide.asp
Kathleen McClaskey is Founder of Make Learning Personal, Co-founder of Personalize Learning, LLC and co-author of bestsellers Make Learning Personal and How to Personalize Learning. She is an innovative leader, education technologist, professional developer, and a Universal Design for Learning (UDL) consultant with over 30 years experience in creating learner-centered environments as a teacher, K-12 administrator and consultant. During this time, Kathleen has presented at national and international conferences on the topics of personalized learning, UDL, learner agency, equity and self-advocacy and is actively involved with Education Reimagined’s Pioneer Lab. She continues on her mission for educators everywhere to discover the learner in every child. You can follow her on Twitter @khmmc or visit her website and blog.